NATO map: meaning of NATO, full members list, history, purpose of the alliance, facts
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) has become a subject of debate since Russia's recent invasion of Ukraine. It is the largest military alliance in the world but has not participated directly in the Russo-Ukrainian war. How well do you know NATO? Herein is everything you need to know regarding the NATO map, history, and purpose.

Source: Twitter
NATO's mandate is to ensure the security and military defence of its members. As of 2022, the military alliance has 30 members. Its expansion into Eastern Europe, including former Soviet states, has caused friction with Russia.
What is NATO?
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization is a political and military alliance consisting of 28 European and 2 North American nations. The North Atlantic Treaty was signed on 4th April 1949 by foreign ministers from 12 countries, including the USA and Western European nations, following the aftermath of WW2. Five months later, the Treaty was endorsed by the parliaments of interested nations, thus sealing the membership.
The Treaty was initially created to offer collective security against the Soviet Union, which refused to participate in the Marshall Plan or allow its satellite states in Eastern Europe to work with the union.
The Marshall Plan had been proposed to ensure stability in the economies of Western European countries that had severely been affected by WW2. It was also to promote cooperation between Europe and the USA.
President Harry S Truman's administration feared Western Europe might negotiate with the Soviets to tackle their security issues. The US then considered the formation of a European-American alliance to enhance security in the West.
The West welcomed the idea of a collective security solution. A resolution was passed to ensure the security treaty adhered to the United Nations charter but existed outside of the Security Council, where the Soviet Union held veto power.
Further negotiations led to the need to expand the Treaty to include the North Atlantic nations. The North Atlantic Treaty was then signed on 4th April 1949 in Washington. Today, NATO is the largest peacetime military alliance globally and includes some former Soviet states.
What are the 30 countries in NATO?

Source: Twitter
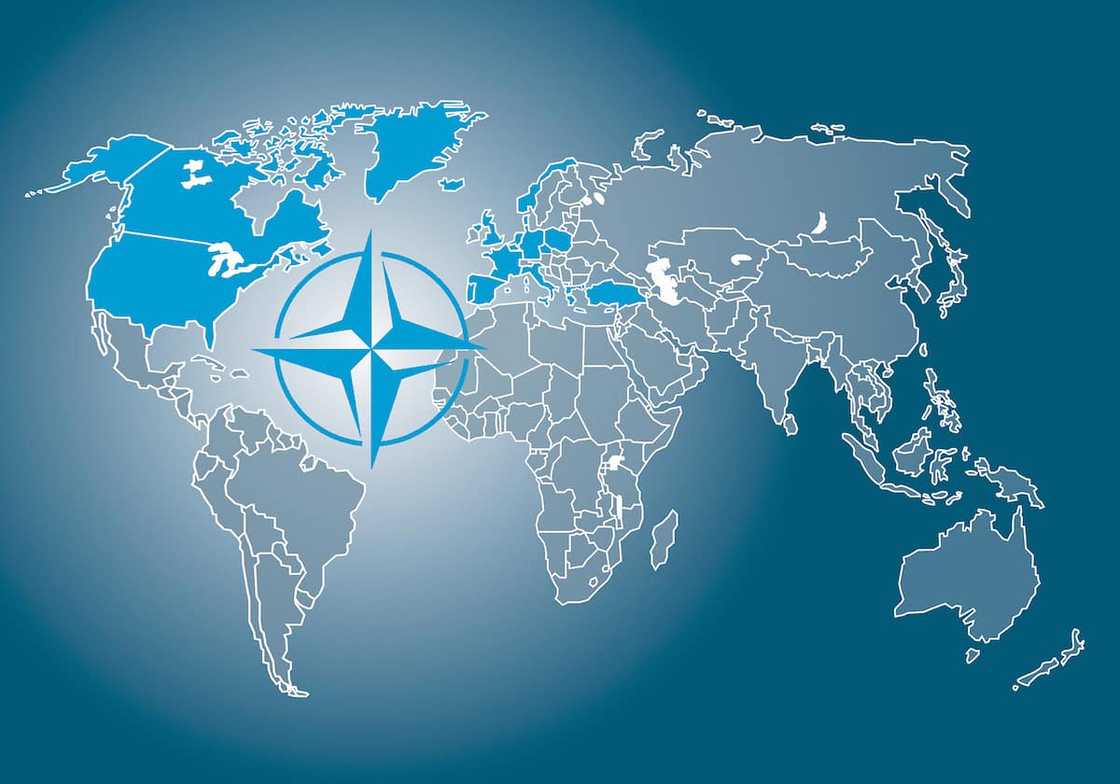
What is NATO territory? The NATO map of 2022 is made up of 30 independent member countries. Below are all the member states and the year they joined;
- Albania (2009)
- Belgium - Founding member
- Bulgaria (2004)
- Canada - Founding member
- Croatia (2009)
- Czech Republic (1999)
- Denmark - Founding member
- Estonia (2004)
- France - Founding member
- Germany (1955)
- Greece (1952)
- Hungary (1999)
- Iceland - Founding member
- Italy - Founding member
- Latvia (2004)
- Lithuania (2004)
- Luxembourg - Founding member
- Montenegro (2017)
- Netherlands - Founding member
- North Macedonia (2020)
- Norway - Founding member
- Poland (1999)
- Portugal - Founding member
- Romania (2004)
- Slovakia (2004)
- Slovenia (2004)
- Spain (1982)
- Turkey (1952)
- United Kingdom - Founding member
- United States of America - Founding member
Source: Getty Images
Article 10 of the North Atlantic Treaty states that membership is open to any European State in a position to further the principles of the Treaty and contribute to the security of the North Atlantic area. The North Atlantic Council, which is NATO's primary political decision-making body, is the one that decides to invite a nation to join the Alliance based on consensus from all members.
NATO members are subject to the obligations of the Treaty, but they are allowed some form of flexibility. For example, Iceland, which was a founding member in 1949, has never had armed forces until the present.
What is the purpose of NATO?
According to the 2010 Strategic Concept, the Alliance's primary purpose is to ensure collective defence, crisis management, and cooperative security of member states through military and political resolutions. Politically, the Treaty promotes democratic values and prevents possible conflict. Member countries often consult on security and defence affairs, and all NATO decisions are taken by consensus.
The Treaty is committed to fostering peaceful conflict resolution, and if diplomatic relations fail to work, it has the military power to engage in crisis-management operations. NATO is committed to the principle of collective defence, which states that an attack against one or several of its member states is considered an attack against the entire Alliance.
The collective defence clause is contained under Article 5 of the Washington Treaty, and it states;
The Parties agree that an armed attack against one or more of them in Europe or North America shall be considered an attack against them all and consequently they agree that, if such an armed attack occurs, each of them, in exercise of the right of individual or collective self-defence recognised by Article 51 of the Charter of the United Nations, will assist the Party or Parties so attacked by taking forthwith, individually and in concert with the other Parties, such action as it deems necessary, including the use of armed force, to restore and maintain the security of the North Atlantic area.
Since NATO's inception, Article 5 has been effected once during the 2001 9/11 terrorist attacks in the USA. Crisis management operations are also carried out under a United Nations mandate.
NATO partnerships
The military alliance works with more than 40 non-member nations from Central and Eastern Europe as well as the Asia-Pacific region. It is involved with international organizations, including the EU and the UN, to strengthen security outside NATO territory. Partner countries contribute to NATO operations but have limited decision making power.
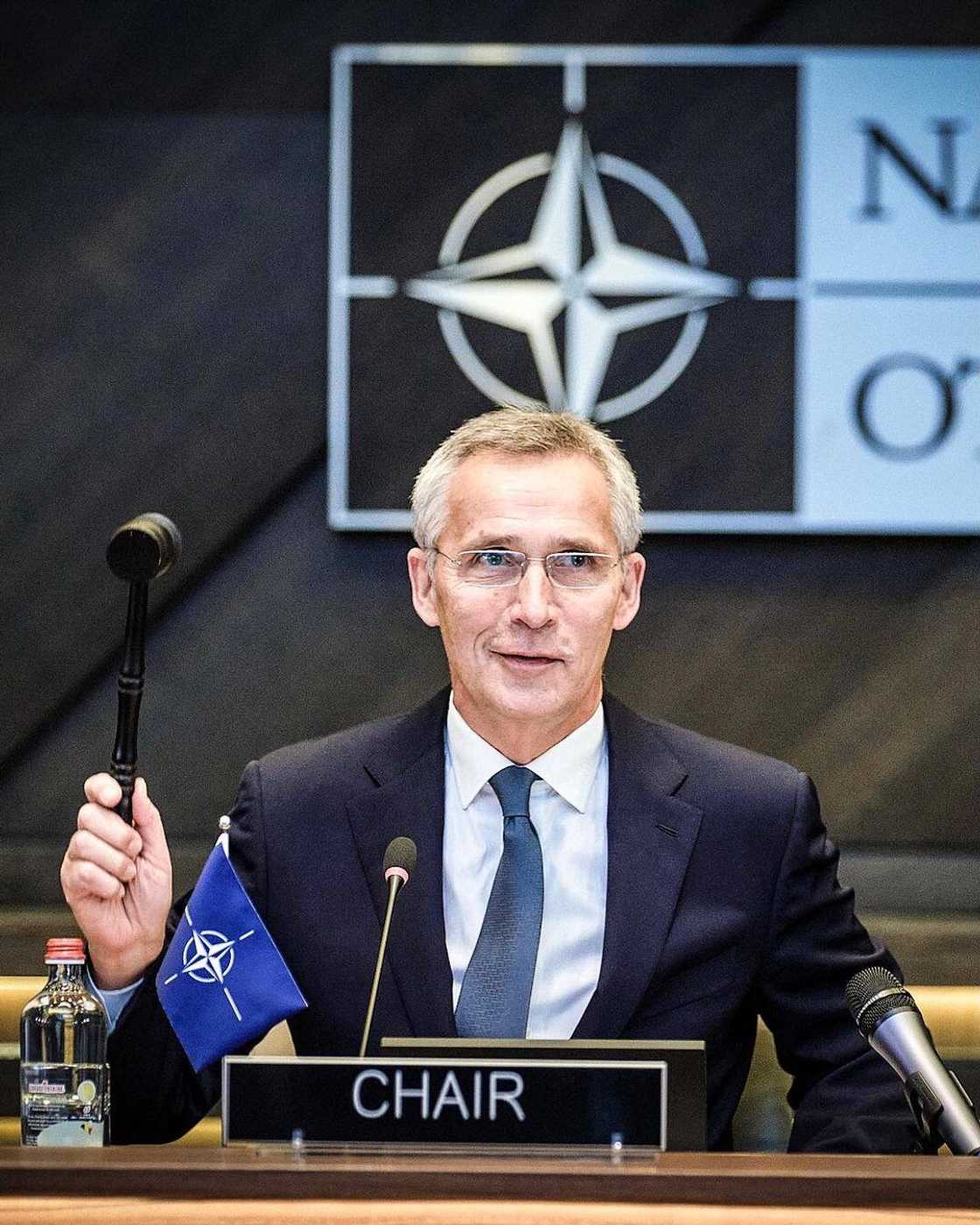
NATO structure

Source: Instagram
The North Atlantic Council (NAC) is the primary political decision-making body of the alliance. It is headed by the Secretary-General, currently being held by Jens Stoltenberg. All the member countries are represented at the NAC, which often holds NATO delegations at the NATO headquarters in Brussels, Germany.
The Nuclear Planning Group has the same power as the NAC when it comes to nuclear policies. The Military Committee is involved in making political decisions that have military implications. It consists of the Chiefs of Defence of NATO members, the International Military Staff, the executive body, and the military command structure.
The members often make a voluntary contribution of their military forces to the alliance since NATO has limited permanent forces.
NATO also has several subordinate committees with experts and representatives from all NATO members. They occasionally meet to tackle more technical matters.
US allies map
The United States has diplomatic relations with most countries across the world. These include NATO members and its allies, Kosovo, the EU, UN member and observer states excluding Bhutan, Iran, North Korea, and Syria. The USA does not recognize the UN observer State of Palestine.
Why is Sweden not in NATO?
The Swedish government value neutrality in a potential war and has a foreign policy on non-participation in military alliances. No war has been engaged in by Sweden since 1814 and was neutral throughout World War 2 and the Cold War. European Union members who have also declared their non-alignment with military alliances are Austria, Finland, Cyprus, Malta, and Ireland.
However, Sweden and its sister country Finland have close cooperation with NATO. Since Russia invaded Ukraine, there have been speculations that the two nations will seal their membership with the military alliance.
The Swedish centre-right opposition has been in support of the country joining NATO. However, the Social Democrats, nationalist Sweden Democrats, the Greens, and the Left Party continue to oppose such a decision.
Since 1949, the NATO map has gradually expanded. Several Eastern European nations, including Ukraine, have shown interest in joining the military alliance, but Russia has opposed the move.
READ ALSO: Who are the 10 worst presidents, and why are they scorned for their leadership?
Briefly.co.za published the top 10 worst presidents in American history. These leaders are known for making questionable leadership policies that plunged the country into chaos. Most of them were partly responsible for the circumstances that led to the Civil War.
A 2021 C-SPAN survey conducted by 142 historians and professional observers of the presidency ranked James Buchanan as the worst leader. Donald Trump is ranked the 4th worst president.
Source: Briefly News

