14 famous philosophers and their principles and influence on the world
In the vast landscape of human thought, famous philosophers have played a pivotal role in shaping how people perceive the world, influencing societal norms, ethics, and intellectual discourse. This article delves into the enduring legacies of 14 philosophers often considered the greatest thinkers of all time.

Source: Getty Images
Philosophy is a discipline that seeks to understand the underlying principles governing various aspects of human experience and the world. Throughout history, there have been numerous influential philosophers. Different cultures and periods have produced a rich tapestry of philosophical ideas and perspectives.
World famous philosophers and scientists
The great philosophers highlighted below have left an indelible mark on the world. The listing is not in any particular order since all their works have an immeasurable influence.
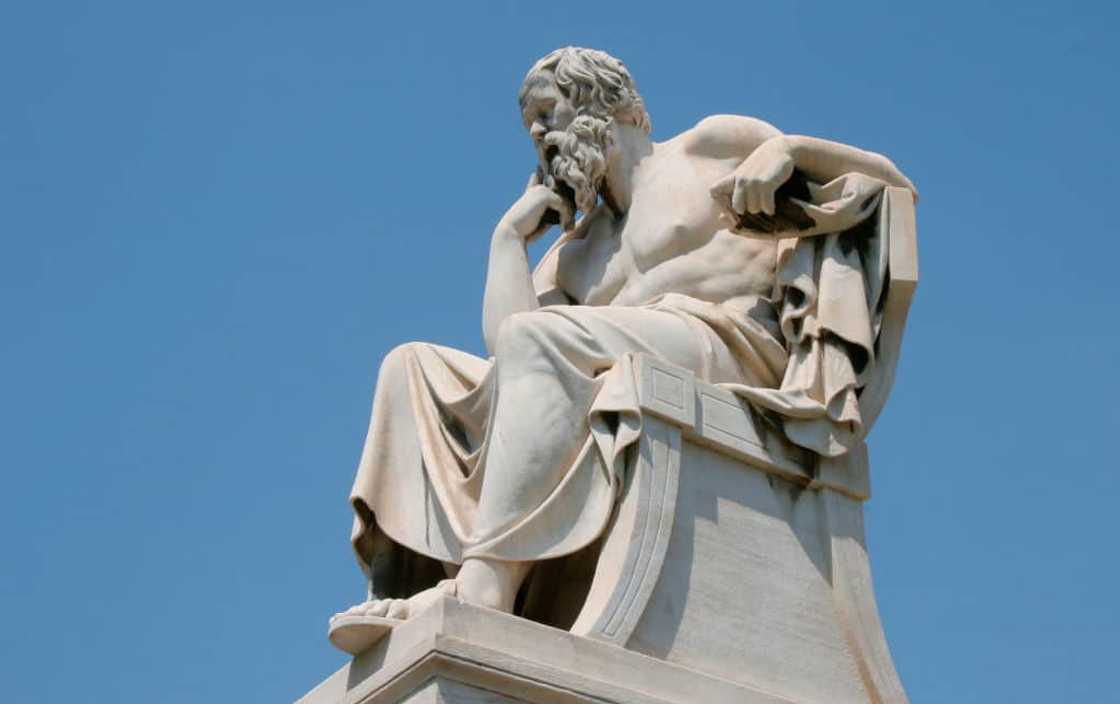
1. Socrates (469-399 BC)

Source: Getty Images
Socrates was a classical Greek philosopher credited as one of the founders of Western philosophy. His ideas laid the groundwork for ethical philosophy and dialectical reasoning. His teachings profoundly impacted his students, especially Plato, whose dialogues often feature Socrates as the main character.
Socrates was constantly accused of corrupting the youth and impiety, but he chose a death sentence rather than renounce his philosophical convictions. His fundamental principles include;
- The Socratic Method (A method of questioning): Instead of providing answers, he engaged in dialogue with others, asking questions to stimulate critical thinking and uncover deeper insights.
- Ignorance and wisdom: He argues that he was wise only in knowing that he knew nothing and emphasized the importance of intellectual humility and the continual pursuit of knowledge.
- Moral philosophy: He believed that the key to living a virtuous life was understanding what virtue truly is.
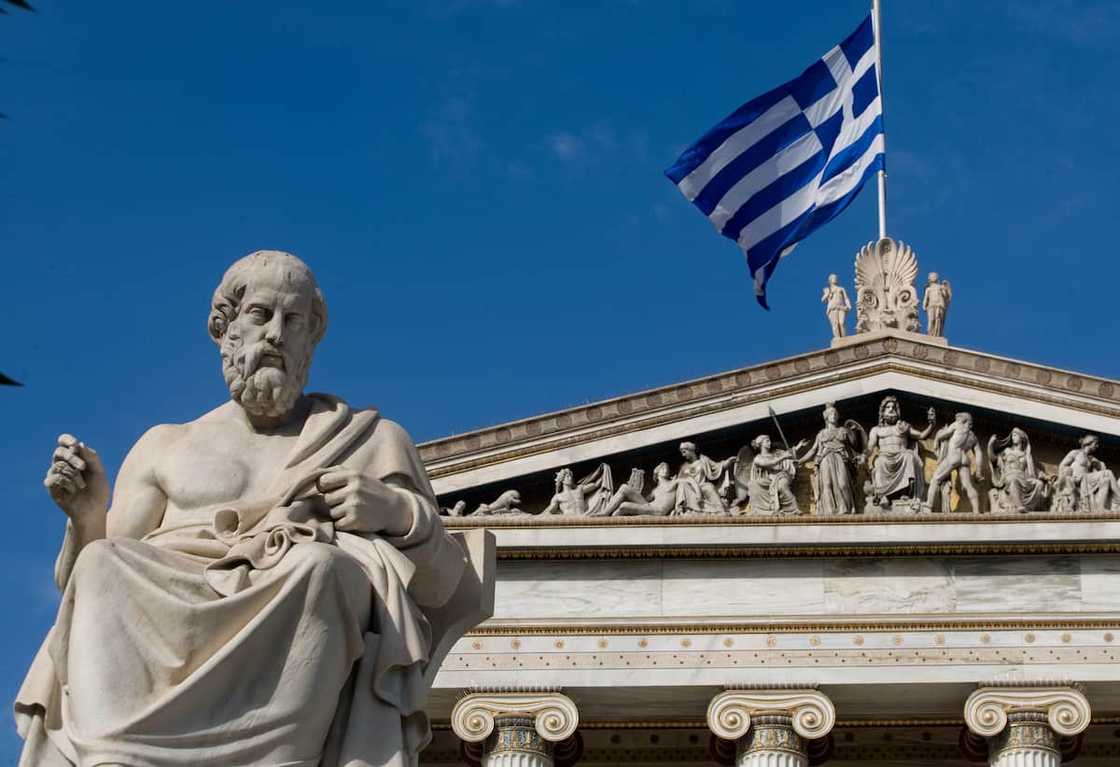
2. Plato (427-347 BC)

Source: Getty Images
Plato was a Greek philosopher who was a devoted follower of Socrates and a teacher of Aristotle. His works are written in dialogues and explore various topics like ethics, politics, metaphysics, and epistemology.
Plato's fundamental principles include;
- The Theory of Forms: He argued that the material world is an imperfect reflection of a higher realm of abstract, perfect, and eternal forms.
- Allegory of the Cave: He explored the journey from ignorance to knowledge, emphasizing the transformative power of education.
- Philosopher-King and ideal state: He envisioned an ideal state governed by philosopher-kings, i.e. individuals who possessed wisdom and a deep understanding of the Forms.
- Tripartite soul: He divided the tripartite soul into reason, spirit, and desire and explored how the elements interact and influence human behaviour.
3. Aristotle (384-322 BC)
Source: Getty Images
Aristotle, a Greek philosopher, was a student of Plato and a teacher of Alexander the Great. He significantly contributed to various fields like science, metaphysics, philosophy, politics, and ethics. Aristotle's fundamental principles include;
- The Doctrine of the Mean: Aristotle believed the best way to live was to find the right balance between extremes. Every virtue is a mean between two extremes, one of excess and one of deficiency.
- The Four Cardinal Virtues: He believed that the four cardinal virtues, prudence, temperance, courage, and justice, are interconnected and essential for achieving eudaimonia, i.e. the highest human good.
- The Three Principles of Argument: Aristotle proposed that there were three principles used in making an argument: ethos, pathos, and logos. A good argument would contain all three.
4. Confucius (551-479 BC)

Source: Getty Images
Confucius was a Chinese philosopher and the founder of the ethical teaching called Confucianism. His teachings have greatly influenced East Asian ethics, governance, morality, social order, and culture. Some of his fundamental principles include;
- Ren (Benevolence or humaneness): This principle involves compassion, kindness, and a sense of empathy towards others.
- Li (Rituals and etiquette): He believed that adhering to rituals and etiquette fosters a sense of order, respect, and moral integrity in society.
- Xiao (Filial piety): He believed that the respect and obedience children owe to their parents and elders are the foundation of a harmonious society.
5. Laozi (6th century BC)

Source: Getty Images
Laozi was a Chinese philosopher considered to be the founder of Daoism (Taoism), a philosophical and religious tradition that emphasizes living in harmony with the Dao (the natural order of the universe). His book, the Tao Te Ching (or Dao De Jing), is one of the most translated works in world literature.
His other key principles include;
- Wu Wei (Non-action): It means aligning oneself with the natural flow of the Dao and acting spontaneously, without unnecessary effort.
- Yin and Yang: Yin and Yang are complementary opposing forces that are interconnected and interdependent. Balancing them is crucial for achieving harmony.
6. Thomas Aquinas (1225-1274)

Source: Getty Images
Thomas Aquinas was an Italian-Dominican friar, philosopher, and theologian. He is best known for his contributions to scholasticism, a philosophical and theological system that sought to reconcile faith and reason.
The principle of scholasticism aimed to harmonize Christian theology with classical philosophy, particularly the works of Aristotle. Aquinas is also known for Summa Theologica, in which he addresses various topics like the existence of God, ethics, metaphysics, and the nature of the human soul.
7. Niccolò Machiavelli (1469-1527)

Source: Getty Images
Niccolo Machiavelli was an Italian Renaissance political philosopher, diplomat, and writer. He is best known for his book, The Prince (Il Principe), considered one of the most influential works on political theory.
Machiavelli's key principles include;
- Realpolitik (The ends justify the means): He argued that rulers should prioritize the stability and power of their states, even if it requires actions that might be considered morally dubious.
- Realism in politics: He emphasized the importance of understanding politics as they are rather than as they should be in an idealized sense. Politicians should be practical and willing to employ whatever means necessary to achieve and maintain power.
- Moral relativism in politics: He argued that political actions should be evaluated based on their effectiveness in achieving desired outcomes rather than being judged by moral or ethical principles.
8. René Descartes (1596-1650)
Source: Getty Images
Rene Descartes was a French philosopher, mathematician, and scientist widely recognized as the father of modern Western philosophy. His emphasis on reason and scepticism continues to shape discussions in various fields.
Descartes' key principles include;
- Cogito, ergo sum (I think, therefore I am): He sought to doubt everything that could be doubted and realized that the act of doubting itself presupposes a thinking self.
- Dualism: He proposed that the mind (or soul) and the body are distinct substances.
- Mathematical method: Descartes made significant contributions to analytic geometry. He applied mathematical principles to philosophy and science, emphasizing the importance of clear and distinct ideas as a foundation for knowledge.
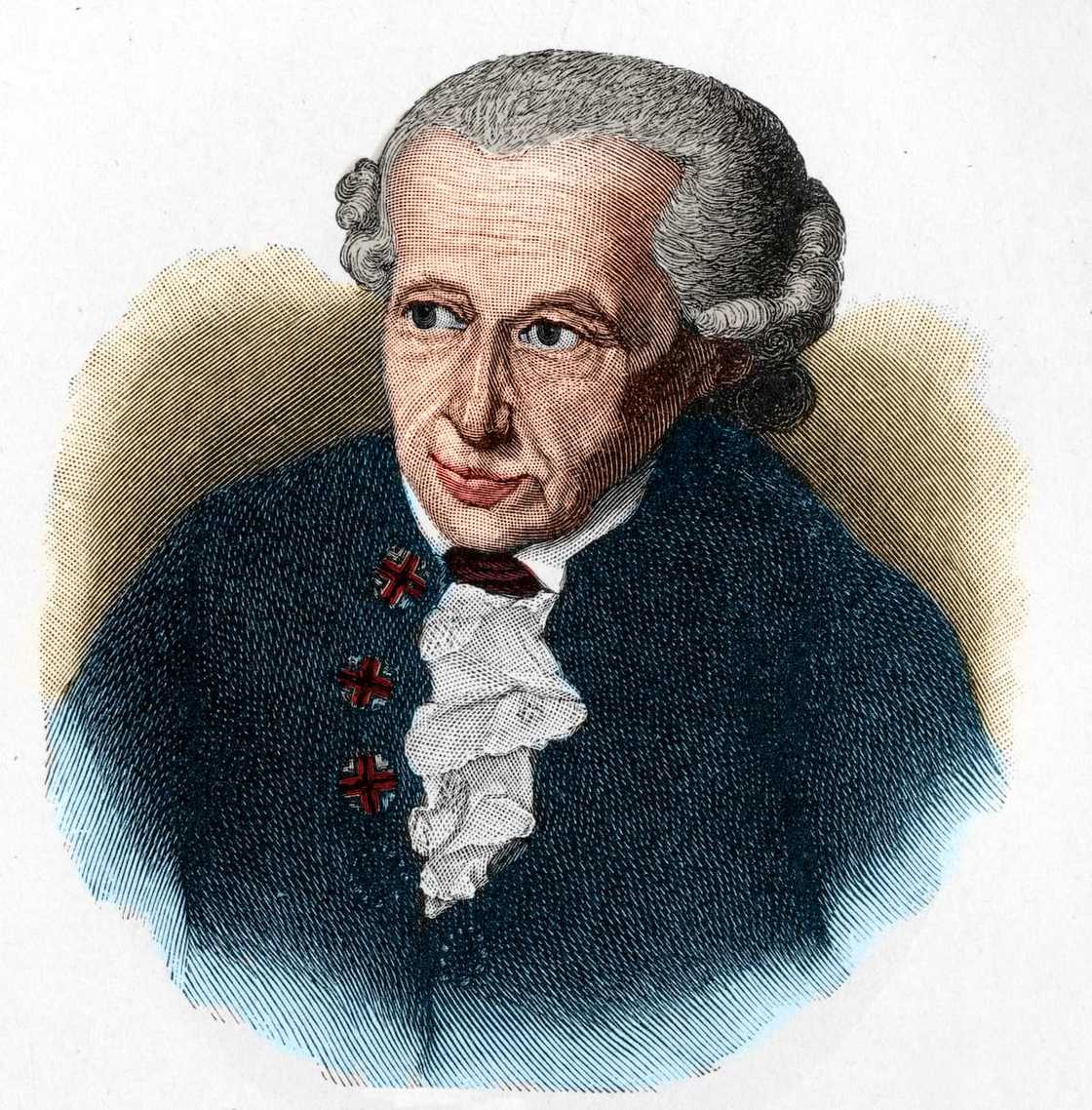
9. Immanuel Kant (1724-1804)

Source: Getty Images
Immanuel Kant was a German philosopher whose ideas profoundly impacted various fields like ethics, metaphysics, epistemology, aesthetics and politics. His work is characterized by his emphasis on reason, morality, and human autonomy.
Kant's key principles include:
- Critique of pure reason: He explores the nature of human knowledge, arguing that certain aspects of knowledge are innate (a priori) and others are derived from experience (a posteriori).
- Copernican Revolution in philosophy: He compared his philosophical shift to the Copernican Revolution in astronomy. Instead of assuming that human knowledge must conform to an independently existing reality, Kant proposed that our cognitive faculties structure and shape our experience of reality.
- Autonomy and freedom: He argued that individuals, as rational beings, can legislate moral laws for themselves.
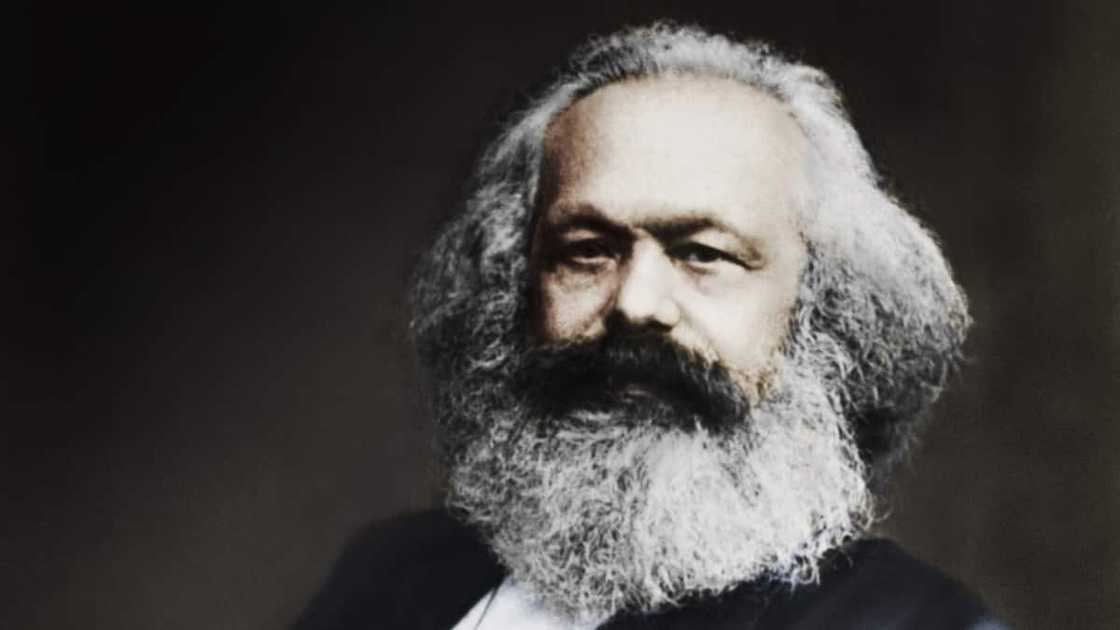
10. Karl Marx (1818-1883)

Source: Getty Images
Karl Marx was a German philosopher, economist, and political theorist. He is widely recognized for his contribution to Marxism, a social, political, and economic theory emphasizing the struggle between capitalists and workers.
His ideas profoundly impacted political and economic thought, leading to the development of Marxist theory and socialist movements. Some of Karl Marx's key principles include;
- Historical materialism: He argued that the material conditions of production determine the development of society.
- Dialectical materialism: This principle asserts that social development occurs through contradictions and conflicts in the material world, leading to qualitative societal changes.
- Class struggle: Marx argued that throughout history, societies have been characterized by the struggle between different classes—typically, the bourgeoisie (owners of the means of production) and the proletariat (working class). He believed the conflict would eventually lead to the overthrow of capitalism.
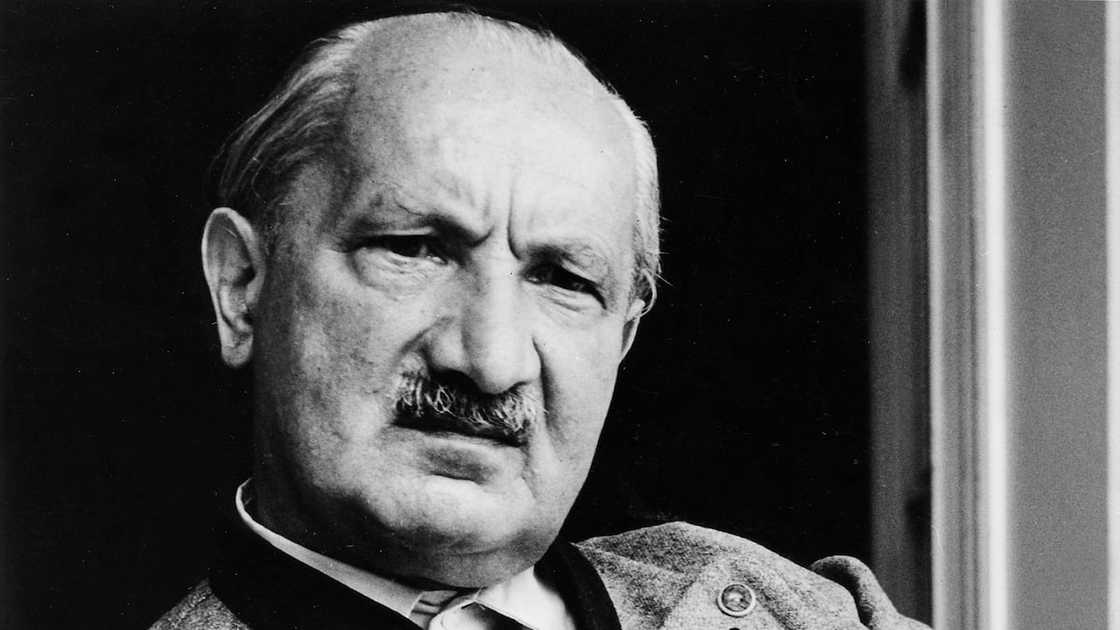
11. Martin Heidegger (1889–1976)

Source: Getty Images
Martin Heidegger was a 20th-century German philosopher who significantly contributed to existential phenomenology and hermeneutics. He believed that the meaning of existence was rooted in individual experience and that authentic living required confronting the inevitability of death. Some of Martin Heidegger's key principles include;
- Sein und Zeit (Being and time): He explores the nature of being and the fundamental structures of human existence.
- Ontology and existential analysis: He argued that traditional philosophy had overlooked the question of being and emphasized the need for a more authentic understanding of human existence.
- Temporal existence: He emphasized the temporal nature of human existence. Time is not just a linear progression but a dynamic structure that shapes our experience.
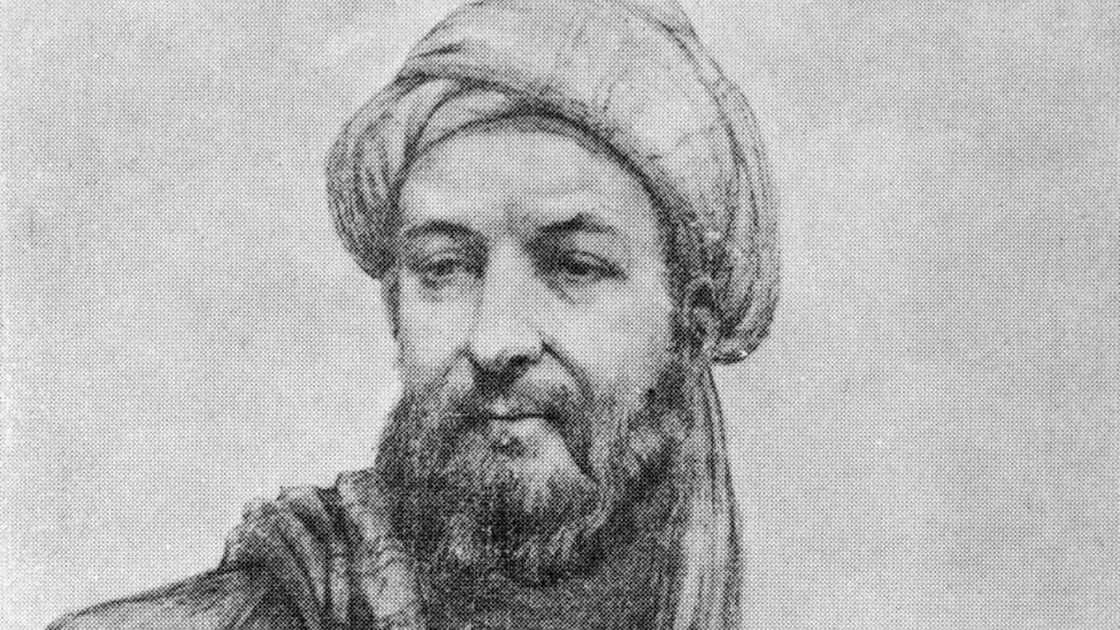
12. Avicenna (980–1037)

Source: Getty Images
Avicenna, also called Ibn Sina, was a Persian polymath regarded as one of the most significant thinkers and writers of the Islamic Golden Age. He contributed substantially to medicine, mathematics, astronomy, philosophy, and science.
Key Avicenna's key works and principles include;
- Kitab al-Shifa (The Book of Healing): A comprehensive compilation that covers a wide range of topics, including metaphysics, logic, ethics, and natural philosophy
- Kitab al-Hikmah (The Book of Wisdom): It focused on theology
- Kitab al-Nafs (The Book of the Soul): He contributed significantly to philosophical psychology, exploring topics like the nature of the soul, its immortality, and the relationship between the soul and the body.
- Neoplatonism and Aristotelianism: He combined ideas from classical Greek philosophy with Islamic intellectual traditions by harmonizing the teachings of Aristotle with Neoplatonic metaphysics.
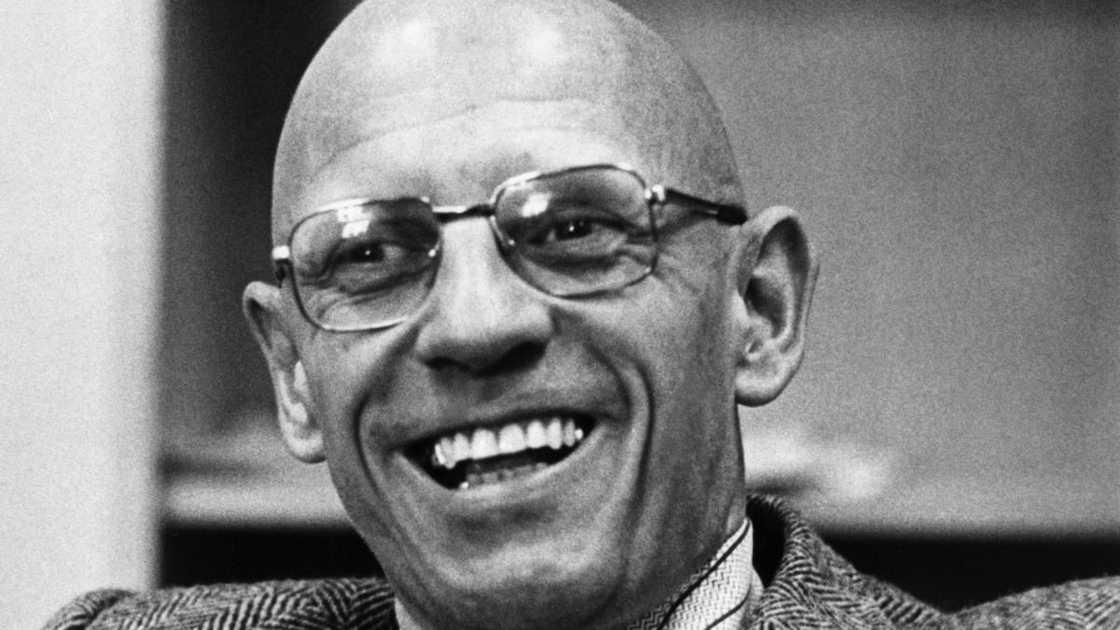
13. Michel Foucault (1926–1984)

Source: Getty Images
Michael Foucault was a French philosopher, social theorist, and historian who significantly contributed to the development of postmodernism. His work continues to influence various disciplines like sociology, cultural studies, and political science.
Some of Michel Foucault's key principles include;
- Power and knowledge: He argued that power and knowledge are closely intertwined and that knowledge is often used as a tool of power.
- Discourse analysis: He examined how language and communication shape our understanding of reality and how discourses construct and maintain societal power structures.
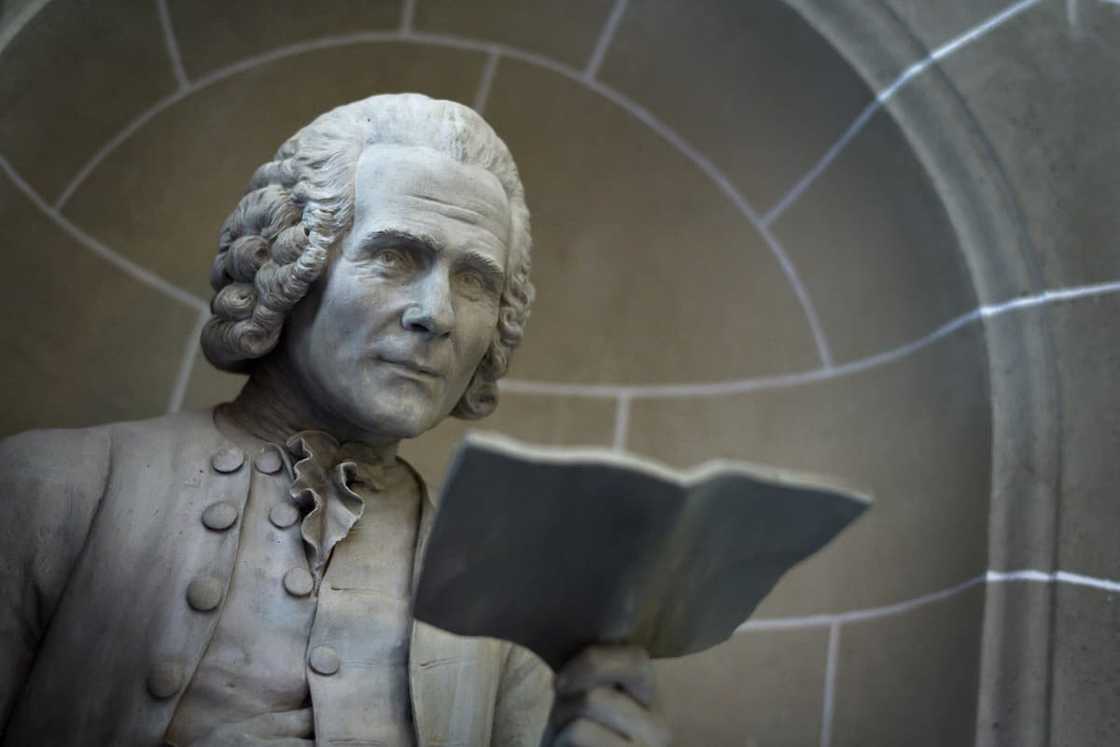
14. Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712-1778)

Source: Getty Images
Jean-Jacques Rousseau was a Swiss philosopher, political theorist and writer known for his contributions to political philosophy, education, and literature during the Enlightenment era. His ideas influenced the French Revolution and thinkers like Immanuel Kant, John Locke, and Karl Marx. Some of Jean-Jacques Rousseau's key principles include;
- Social contract: He proposed that individuals form a social contract with each other to create a political community.
- State of nature: He argues that humans were initially peaceful and egalitarian, but the advent of private property and societal inequalities led to the emergence of political institutions.
- General will: He argued that citizens should act per the general will for the well-being of society.
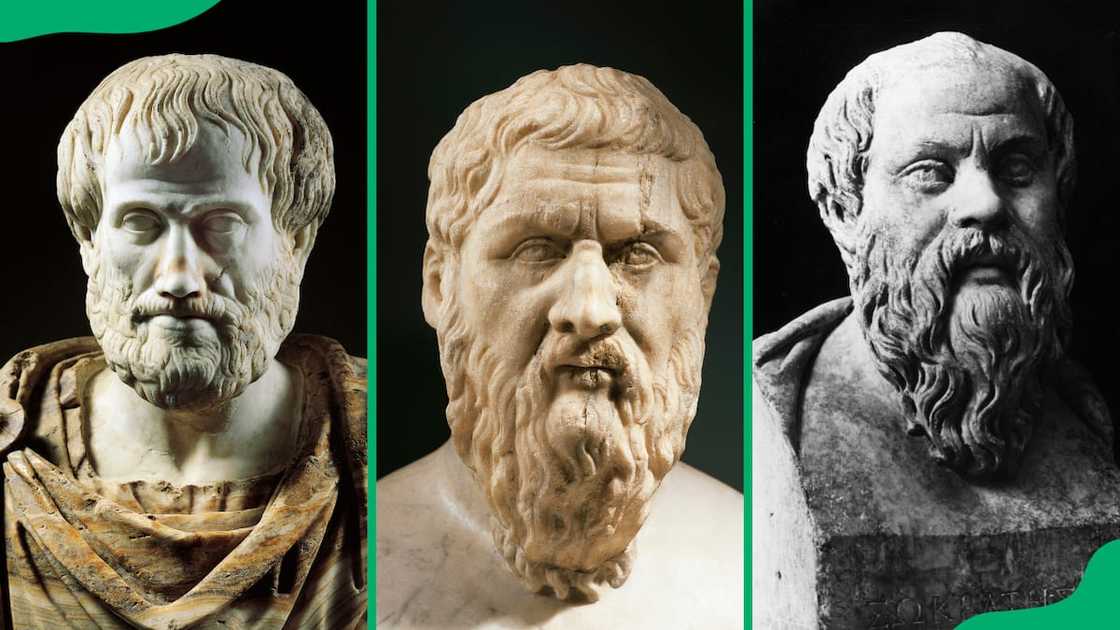
Who are the three most famous Greek philosophers?
The three most famous Greek philosophers include Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle. They are often called the triumvirate of ancient Greek philosophy.

Source: Getty Images
Who is the real father of modern philosophy?
Rene Descartes (1596-1650) is considered the father of modern philosophy. The French philosopher and mathematician significantly contributed to the transition from medieval Scholastic philosophy to the early modern period.
What is Socrates' main philosophy?
Socrates' main philosophy is based on the Socratic method of questioning and how dialogue can uncover knowledge. He also argued that individuals only commit virtuous acts if they understand what is good and evil. Socrates did not leave behind any written works, but his ideas were conveyed through dialogues written by his student Plato.
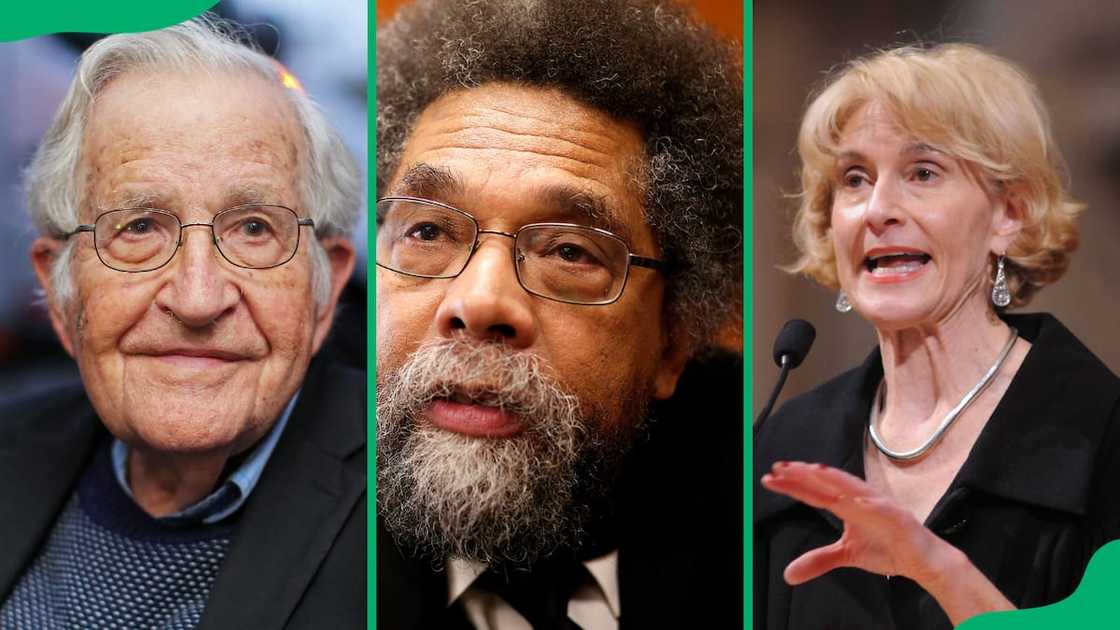
Who are the best philosophers in the world today?
Some of the top philosophers today include;
- Noam Chomsky: He is an American professor, philosopher, linguist, historian, cognitive scientist, and political activist. He is regarded as one of the most influential thinkers of the 20th century and is often referred to as the father of modern linguistics.
- Slavoj Žižek: He is a Slovenian philosopher, cultural critic, and psychoanalytic theorist. He is known for his provocative and interdisciplinary approach to film theory, psychoanalysis, politics, and popular culture.
- Cornel West: He is an American professor, philosopher, political activist, author, and public intellectual. He is best known for his contributions to critical theory, race theory, and political philosophy.
- Martha Nussbaum: She has significantly contributed to virtue ethics, political philosophy, philosophy of emotions, and capabilities approach, i.e. a theoretical framework for understanding well-being and development.
- Judith Butler: She is a philosopher and gender studies scholar. She has made significant contributions to gender theory and queer studies.

Source: Getty Images
The legacy of the famous philosophers highlighted above continues to influence modern thought. The list is not exhaustive; many other scholars have made and continue to contribute to the field.
READ ALSO: 15 funny bedtime stories for your girlfriend to make her smile
Briefly.co.za highlighted 15 funny bedtime stories you can narrate to your girlfriend. Sleep stories are known for offering a passive pastime that can ease your journey to dreamland.
Everyone needs to unwind after a long, busy day, and one of the best forms of relaxation is listening to bedtime stories. Check the article for ideas that will help you prepare your partner for a restful night.
Source: Briefly News









